Categories: NACHA file validator
In a world where fast and secure financial transactions are essential, understanding the ACH payment format is a game-changer for any financial institution. The Automated Clearing House (ACH) serves as the backbone of electronic money movement in the banking industry, facilitating millions of transactions such as direct debits, payroll, and tax payments daily. These transactions are performed using ACH files, the unsung heroes of financial operations.
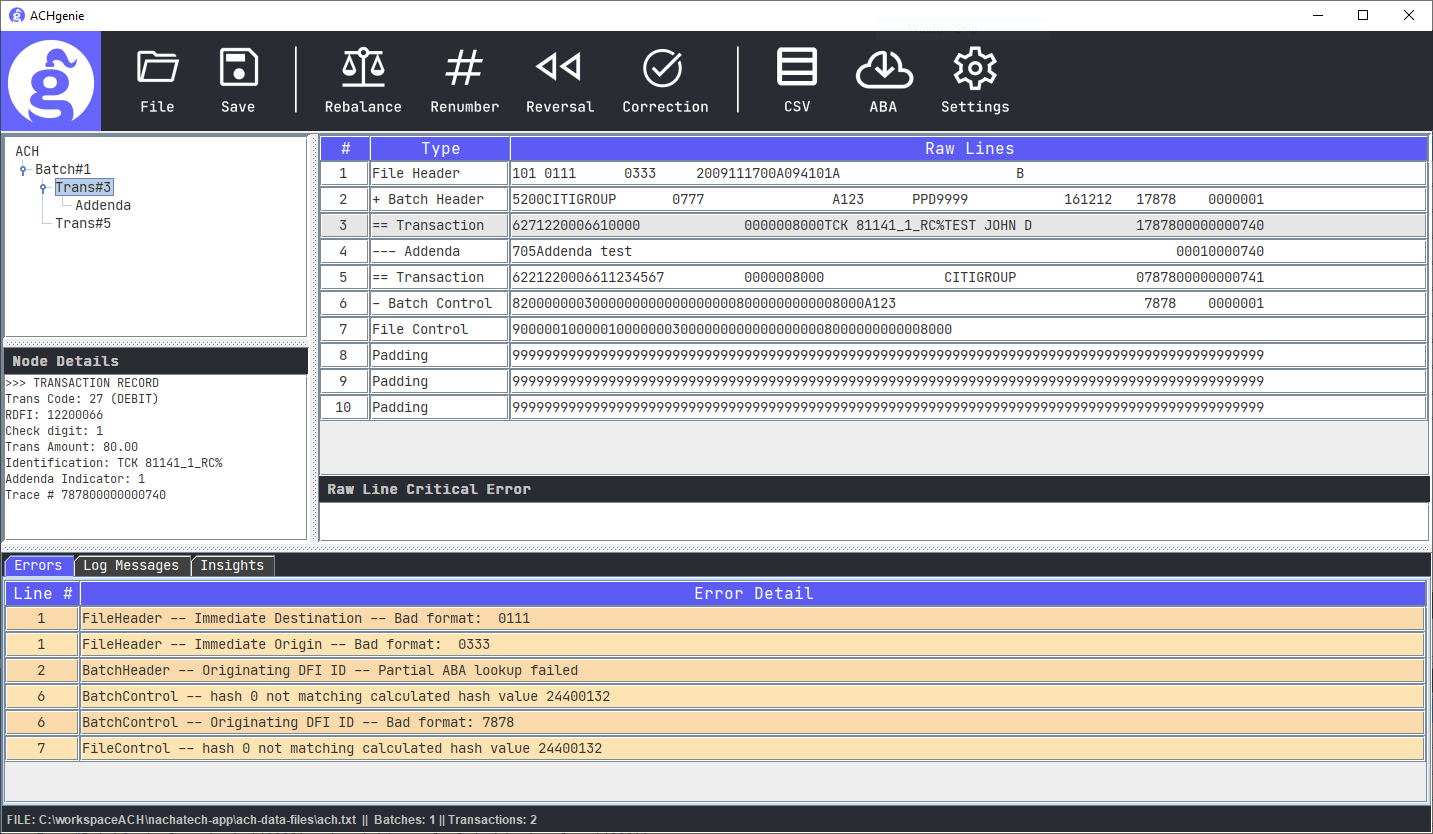
ACH files are fixed-width, ASCII files that hold crucial details for money transfers between banks. Each line, precisely 94 characters long, is known as a “record” and consists of various “fields” at specific positions within the line. These files contain one or more batches, with each batch consisting of one or more transactions. They capture specific data elements at different levels within the file, batch, or transaction, ensuring the secure and efficient processing of each transaction.
In the digital economy of today, the role of ACH files cannot be overstated. They offer a standardized format for transactions, ensuring consistency across different banks and financial institutions. This consistency is key to the seamless processing of transactions, guaranteeing smooth financial operations and stability for businesses.
However, as valuable as ACH files are, they are not without their challenges. Mismanagement or errors in these files can lead to ACH payment rejections, disrupting cash flow and potentially damaging business relationships. Hence, understanding the ACH payment format and learning how to manage these files effectively becomes a critical need for any financial institution.
In this article, we will dive into the intricacies of the ACH payment format, helping you understand its structure, decode the standard entry class (SEC) codes, and comprehend the role of addenda records in ACH files. We will also discuss the importance of ACH number format and how ACH Genie’s file validator can streamline your ACH transactions. Stay tuned to unravel the mysteries of ACH file format and learn how to master its management.
Understanding the ACH File Structure
Mastering the ACH file format is akin to learning an intricate dance; every move has a purpose, and every step carries valuable information. When dealing with ACH files, three crucial elements form the backbone of the structure – the File Header and Footer, the Batch Headers and Footers, and the Detailed Transaction Records.
The Role of File Header and Footer in ACH Files
The File Header Record, identifiable by the digits ‘101’ at the start of the line, serves as the curtain raiser, establishing the identity of the originating bank and providing a timestamp for the transaction. It’s the first line of communication that sets the stage for the following transactions. The File Footer, or the File Control Record, brings the act to a close. Acting like a vigilant gatekeeper, it verifies the integrity of the file by providing counts, sums, and a hash total, ensuring that the file was generated correctly.
The Importance of Batch Headers and Footers
Ensuring smooth ACH transactions is all about getting the details right, and that’s where Batch Headers and Footers come into the picture. The Batch Header Record signifies the start of a new batch of transactions, detailing the type and purpose of the transactions within the batch. It’s like the director’s note before a play, setting the scene and giving context to the act.
On the other hand, the Batch Control Record serves as a curtain call for each batch, summarizing the transactions and ensuring their validity with the help of a hash total. It’s the final bow that brings the act to a close, ensuring all loose ends are tied up neatly.
Detailed Transaction Records: The Core of ACH Files
Now that we’ve set the stage and understood the role of the curtain raiser and closer let’s dive into the heart of the matter – the Detailed Transaction Records. These records, beginning with a ‘6’, contain the specifics of the transaction, such as the receiver’s account details, transaction amount, and type. They’re the main characters of our play, driving the narrative forward.
For more complex transactions, there may be additional Addenda Records to help describe the transaction further. Think of these as the supporting characters – they help to enrich the story and provide vital details to ensure a smooth, error-free transaction.
Understanding the structure and roles of these different elements is pivotal in managing ACH transactions efficiently and reducing the risk of errors. In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the specifics of Standard Entry Class (SEC) codes and their role in ACH files. Stay tuned to continue your journey towards mastering the ACH file format.
Decoding the Standard Entry Class (SEC) Codes
As we navigate the labyrinth of ACH transactions, the Standard Entry Class (SEC) Codes serve as our map, guiding us towards successful transactions. Each SEC code is unique, offering a clear indication of the nature of the transaction, whether it’s single-entry or recurring, and the specific computer record format used. To streamline your ACH transactions, let’s delve into the details of these codes and understand their usage.
ARC (Accounts Receivable Entries): What it Means and When to Use it
The ARC (Accounts Receivable Entries) code represents a single ACH debit used by an originator for converting an eligible source document received via mail, delivery service, or in person, for bill payment. This SEC code is used in transactions where consumer accounts are debited and funds transferred to corporate accounts. The key requirement is that notification must be provided before accepting the check. Understanding when to use the ARC code can significantly reduce errors and ensure seamless transactions.
CCD (Corporate Credit or Debit): A Deep Dive
CCD, or Corporate Credit or Debit, is another commonly used SEC code. It signifies a single or recurring ACH credit or debit originated to a corporate account. This code is typically used for transactions like vendor payments, payroll funding, and cash concentration from outlying accounts. The CCD entry can also include a single addenda record to relay payment-related information. An agreement is required for transfers between companies, with written authorization implied.
PPD (Pre-arranged Payment or Deposit): An Overview
The PPD (Pre-arranged Payment or Deposit) code is used for single or recurring ACH credits or debits initiated by an originator to a consumer account for payment collection or making a payment. The authorization for this transaction type is obtained in writing. Familiarity with the PPD code is crucial as it’s commonly used for direct deposit and direct payments.
WEB (Internet-Initiated/Mobile Entries): Understanding its Use
Last but not least, the WEB code is used for internet-initiated or mobile entries. It encompasses two categories: credit WEB entries, which are person-to-person entries transmitted on behalf of one natural person to another, and debit WEB entries, which are initiated according to an authorization obtained via the internet or a wireless network. For credit WEB entries, no authorization by the receiver is required, while for debit WEB entries, a similarly authenticated standard is followed.
Decoding these Standard Entry Class (SEC) codes is a vital step towards error-free ACH transactions. By understanding their unique characteristics and appropriate uses, you can significantly enhance your ACH transaction processes, reduce errors, and ensure seamless financial operations. In the next section, we’ll explore the role of Addenda records in ACH files. Stay tuned!
The Role of Addenda Records in ACH Files
In the realm of Automated Clearing House (ACH) transactions, Addenda records are like the secret sauce that adds flavor and detail to your payment information. These records serve as an essential component of the ACH file structure, carrying additional payment-related data that extends beyond the basic transaction details. In this section, let’s delve deeper into the role and significance of Addenda records in ACH files.
How Addenda Records Enhance Payment Information
Imagine trying to process a payment without knowing the invoice number or payment action code. It would be like trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces. This is where Addenda records come to the rescue. They can hold up to 80 characters of ANSI ASC X12 information, providing a platform for your ACH files to communicate detailed data about each transaction.
For instance, in Corporate Trade Exchange (CTX) records, Addenda can carry information such as the invoice or reference number, Payment Action Code, amount, total invoice, and discount amount taken. This level of detail enhances not only the transaction’s clarity but also the accuracy, ensuring smooth and error-free processing.
The Use of Tax Addenda Records (TXP) in ACH Transactions
In the context of Prearranged Payment and Deposit Entry (PPD) and Cash Concentration or Disbursement (CCD), an Addenda record can be a powerful tool for transmitting tax-related payment information. A perfect example of this is the Tax Payment (TXP) Banking Convention used in the addendum record of a CCD+ formatted record.
This TXP addendum record can carry vital details such as the Tax Payer’s ID Number, Tax Payment Type, Tax Period End Date, Tax Type, and the corresponding amount. Such information is particularly valuable when making payments to systems like the Federal EFTPS (Electronic Federal Tax Payment System).
In a nutshell, Addenda records lend a helping hand to financial institutions, businesses, and individuals, providing a platform for detailed, accurate, and efficient ACH transactions. In the next section, we will explore the importance of ACH number format and how it contributes to the smooth operation of ACH transactions. Stay connected to unravel more insights about ACH payment formats!
The Importance of ACH Number Format
In the complex labyrinth of financial transactions, the ACH number format serves as a reliable roadmap, guiding your payments to their intended destination. As we navigate through the world of Automated Clearing House (ACH) transactions, understanding the structure and significance of these ACH numbers is a crucial step towards ensuring the seamless processing of financial transfers.
The Structure of ACH Routing Numbers
The ACH routing number, often known as the routing transit number, is a unique nine-digit code assigned to each financial institution in the United States. This number is used to identify the specific bank or credit union involved in a financial transaction. The ACH routing number is typically found at the bottom of a bank check and forms an integral part of the process of routing funds electronically between banks.
The structure of ACH routing numbers is quite standardized. They are always nine digits long, and the first two digits often range from 61 to 72. This number may be the same routing number as the one on your checks, but they can be different, so it’s essential to verify this number with your bank or through your online banking portal before using it.
Verifying ACH Routing Numbers: A Crucial Step
The importance of verifying ACH routing numbers cannot be overstated. An incorrect ABA number can result in payment rejections, delays in transaction processing, and potential financial losses. Therefore, the validation of these numbers is not just a best practice, but a compliance requirement mandated by regulatory bodies like NACHA.
Fast and reliable validation of these numbers is vital. Tools like ACH Genie’s ACH File Validator provide real-time validation using an up-to-date database, ensuring that every ABA number used in your transactions is accurate and valid. By quickly validating ABA numbers, you can ensure the smooth processing of transactions, avoid potential losses, and maintain the trust of your clients.
In the realm of ACH transactions, where the accuracy of ABA numbers is paramount, ACH Genie’s ACH File Validator stands as a trusted tool to streamline your financial transactions. As we continue to explore the nuances of ACH payment formats in the next sections, you will learn more about how ACH Genie’s solutions can help you handle major errors in ACH files and offer fast validation of ABA numbers, ensuring smooth and efficient ACH transactions.
Streamlining ACH Transactions with ACH Genie
Navigating the world of ACH transactions can feel like walking through a maze, but with the right tools, the path becomes clear and manageable. The key to this lies in the capabilities of ACH Genie, a state-of-the-art software solution designed to tackle the intricacies of ACH payment formats.
How ACH Genie Helps in Editing and Validating NACHA Files
ACH Genie takes the complexity out of ACH file management. It serves as a comprehensive tool to open, edit, and validate ACH files, even those with major errors. This robust solution allows businesses to identify and rectify errors with ease, empowering them to prevent potential ACH payment rejections. This proactive approach helps keep the wheels of your business transactions turning smoothly, avoiding the pitfalls of payment rejections that can lead to strained relationships with clients, unnecessary costs, and delayed transactions.
The Unique Selling Point of ACH Genie: Handling Major Errors in ACH Files
The major edge that ACH Genie brings to the table is its capability to handle major errors in ACH files. It’s not just about identifying these errors; it’s about providing the flexibility to rectify them. ACH Genie’s unique raw line editing feature allows businesses to make necessary changes that adhere to NACHA standards. This is a game-changing feature that allows businesses to go beyond the usual constraints and ensure their ACH files are error-free and compliant.
The Benefits of Fast Validation of ABA Numbers with ACH Genie
But the advantages of ACH Genie don’t stop at handling major errors. The software is also equipped with an embedded ABA database that facilitates swift validation of ABA (American Bankers Association) numbers, an essential component of ACH transactions. Incorrect ABA numbers can lead to failed transactions and consequently, ACH payment rejections. With ACH Genie’s rapid validation, businesses can ensure their ACH files contain valid ABA numbers, significantly reducing the chances of ACH payment rejections.
In the complex world of ACH transactions, having a reliable tool to navigate the intricacies of ACH payment formats is invaluable. ACH Genie is more than just a tool; it’s an ally in ensuring smooth, efficient, and successful transactions. From handling major errors to offering fast validation of ABA numbers, ACH Genie provides the edge businesses need to streamline their ACH processing.
As we sail through the digital age, the importance of ACH transactions cannot be overstated. Whether it’s about automating B2B payments, reducing the chances of human error, or accelerating the speed of transactions, ACH payments have undoubtedly transformed the financial landscape. However, the complexities associated with ACH payment formats can sometimes be a hurdle. This is where a Nacha file validator like ACH Genie comes into play, turning this hurdle into a springboard for efficiency and success.
The Game Changer: Nacha File Validator
ACH Genie, with its advanced file validator, provides the perfect solution to these challenges. It not only opens and edits ACH files containing major errors but also provides the capability for raw line editing. This means you can directly modify the ASCII text of the ACH files, ensuring precision and flexibility in your transactions.
Fast Validation of ABA Numbers
A unique feature of ACH Genie is its fast validation of ABA numbers. This validation ensures that the routing numbers used in the transactions are accurate, thereby reducing the chances of rejections. With ACH Genie, you no longer have to worry about incorrect ABA numbers causing a delay in your transactions, as the software swiftly validates these numbers, ensuring a smooth transaction process.
Handling Major Errors in ACH Files
ACH Genie stands out in its ability to handle major errors in ACH files. It’s not just about identifying the errors; ACH Genie goes a step further to rectify these errors, ensuring that your ACH files comply with the regulatory standards. This ability to handle and rectify major errors sets ACH Genie apart in the realm of ACH payment processing.
In Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial transactions, ACH Genie’s Nacha file validator stands as a beacon of efficiency and reliability. It not only simplifies the complexities of ACH payment formats but also streamlines the transaction process, ensuring a seamless financial operation. With its advanced features and user-friendly interface, ACH Genie is indeed a game-changer, making ACH transactions a breeze. So, whether you’re a financial institution, a business owner, or simply a user dealing with ACH payments, it’s time to embrace ACH Genie and experience a smooth sail in the sea of ACH transactions.